Financial planning is the process of managing your money to achieve your life goals. Whether it’s buying a home, funding education, starting a business, or retiring comfortably, financial planning provides a structured roadmap to make your aspirations a reality. While many people think of finance as simply saving or investing, true financial planning is comprehensive and strategic. It involves assessing your current financial situation, defining short- and long-term goals, and creating actionable steps to reach them.
The Importance of Financial Planning
Without a plan, money management can be haphazard and stressful. Financial planning helps individuals make informed decisions about spending, saving, and investing. It gives clarity about priorities and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently. Furthermore, it provides a sense of security, as you are prepared for unexpected expenses or emergencies.
One of the key benefits of financial planning is reducing financial stress. Knowing that you have a plan in place can improve mental well-being, allowing you to focus on your personal and professional life without constantly worrying about money. It also enables better decision-making by helping you evaluate trade-offs and make choices aligned with your goals.
Core Components of Financial Planning
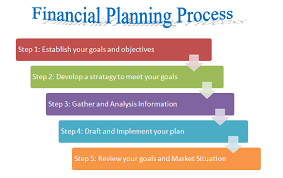
Financial planning consists of several interconnected components. Each element plays a crucial role in building a solid financial foundation.
1. Assessing Your Financial Situation
The first step in financial planning is understanding where you currently stand. This involves analyzing your income, expenses, debts, and assets. Creating a detailed record of your financial situation helps identify areas for improvement and opportunities for growth.
A clear understanding of your finances allows you to set realistic goals. For instance, if a large portion of your income goes toward unnecessary expenses, budgeting can free up resources for saving and investing. Assessing your current financial situation is the foundation upon which the rest of your financial plan is built.
2. Setting Financial Goals
Goals give your financial planning direction and purpose. These can be short-term, medium-term, or long-term:
- Short-term goals might include creating an emergency fund, paying off credit card debt, or saving for a vacation.
- Medium-term goals could involve buying a car, starting a small business, or funding higher education.
- Long-term goals typically focus on retirement, buying a home, or achieving financial independence.
Well-defined goals should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This approach ensures that your objectives are clear and attainable.
3. Budgeting and Managing Cash Flow
Budgeting is the process of planning how to spend and save your money each month. A budget helps track income, prioritize expenses, and identify opportunities to save. Proper cash flow management ensures that you are not overspending and can consistently allocate funds toward your goals.
Budgeting is not just about restricting spending; it’s about making conscious choices. By analyzing your expenses, you can eliminate unnecessary costs, redirect funds toward investments, and ensure that you live within your means.
4. Saving and Investing
Saving is essential for short-term needs, while investing is crucial for long-term growth. Financial planning requires a balance between the two. Emergency savings should cover at least three to six months of living expenses. Beyond that, investing in assets like stocks, bonds, or mutual funds can help your money grow over time.
Investment planning involves assessing risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. Diversifying your investments reduces risk and increases the potential for returns. It is also important to regularly review your portfolio to ensure it aligns with changing goals and market conditions.
5. Managing Debt
Debt is a common part of modern life, but unmanaged debt can hinder financial progress. Effective financial planning includes strategies to manage and reduce debt. This might involve consolidating high-interest debts, negotiating better terms, or prioritizing repayment of costly loans.
Maintaining a healthy credit score is another critical aspect of debt management. A good credit score can reduce borrowing costs and make financial transactions smoother.
6. Risk Management and Insurance
Life is unpredictable, and financial planning must account for uncertainties. Insurance is a tool to mitigate risk. Health insurance, life insurance, disability insurance, and property insurance provide financial protection against unforeseen events.
Without proper risk management, unexpected emergencies can derail your financial goals. A well-structured financial plan incorporates insurance coverage as a safeguard, ensuring that a single event does not cause financial instability.
7. Retirement Planning
Retirement planning ensures that you have sufficient resources to live comfortably after you stop working. It involves estimating future expenses, understanding social security benefits, and creating investment strategies to build a retirement corpus.
The earlier you start planning for retirement, the more you can take advantage of compounding interest. Regular contributions to retirement accounts, combined with smart investment choices, can secure a financially independent future.
8. Estate Planning
Estate planning is the process of organizing your assets to ensure they are distributed according to your wishes after your death. This includes creating a will, setting up trusts, and naming beneficiaries. Estate planning also helps minimize taxes and legal complications for your heirs.
Even if you are young, estate planning is important. It provides clarity and reduces potential disputes, giving you and your family peace of mind.
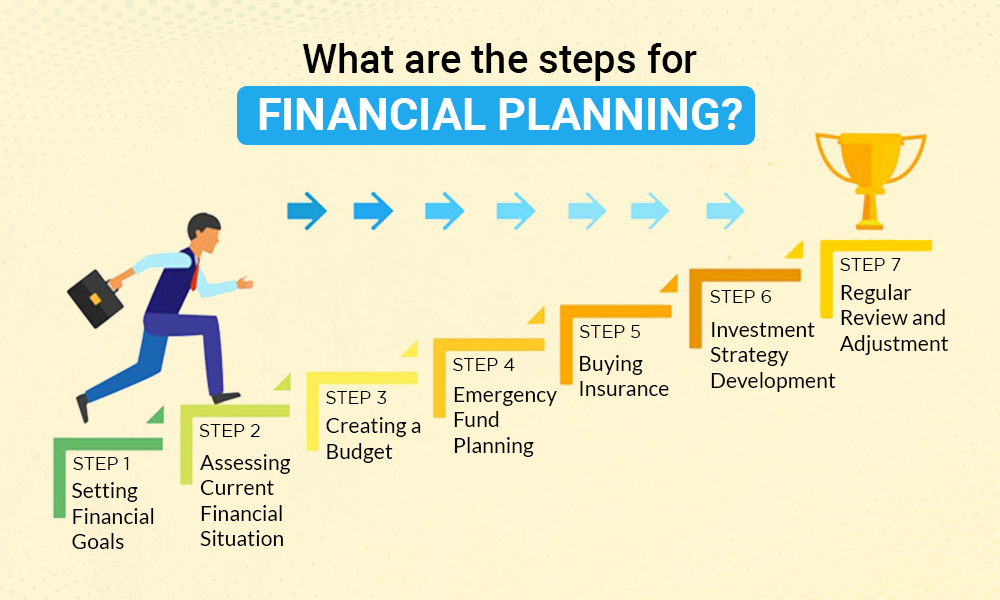
Steps to Create a Financial Plan
Creating a financial plan may seem complex, but it can be broken down into simple, actionable steps:
- Evaluate your current financial position – List all assets, liabilities, income, and expenses.
- Define clear financial goals – Short-term, medium-term, and long-term objectives.
- Develop a budget and cash flow plan – Track spending and allocate funds wisely.
- Establish an emergency fund – Save three to six months of living expenses.
- Formulate an investment strategy – Diversify investments based on risk and time horizon.
- Manage debts – Prioritize repayment and avoid high-interest borrowing.
- Plan for retirement – Start early and regularly contribute to retirement accounts.
- Review and adjust the plan regularly – Life changes, and so should your financial plan.
Common Mistakes in Financial Planning
While financial planning offers numerous benefits, common mistakes can hinder progress:
- Ignoring budgets: Without monitoring spending, goals can become unreachable.
- Delaying saving and investing: Procrastination reduces the power of compounding.
- Overlooking insurance: Lack of coverage can result in financial setbacks.
- Focusing solely on short-term goals: Long-term planning is essential for stability.
- Failing to update the plan: Financial plans must adapt to life events and market changes.
Avoiding these mistakes requires discipline, awareness, and a proactive approach.
The Role of a Financial Planner
While self-education is valuable, a professional financial planner can offer expertise and personalized guidance. Financial planners analyze your situation, recommend strategies, and help implement a comprehensive plan. They can also provide insights into tax planning, investment management, and retirement strategies.
A good financial planner does more than just give advice—they partner with you to achieve financial security and independence.
Conclusion
Financial planning is not just for the wealthy; it is essential for anyone who wants to take control of their financial future. By understanding your current situation, setting clear goals, managing money wisely, and planning for uncertainties, you can achieve stability and peace of mind.
The process may require effort and discipline, but the rewards are invaluable. A well-crafted financial plan empowers you to make informed decisions, reduce stress, and pursue your life goals confidently. Remember, financial planning is a journey, not a destination. The earlier you start, the stronger your foundation will be for a secure and prosperous future.




